Adaptive Online Decision Method for Initial Congestion Window in 5G Mobile Edge Computing Using Deep Reinforcement Learning
摘要
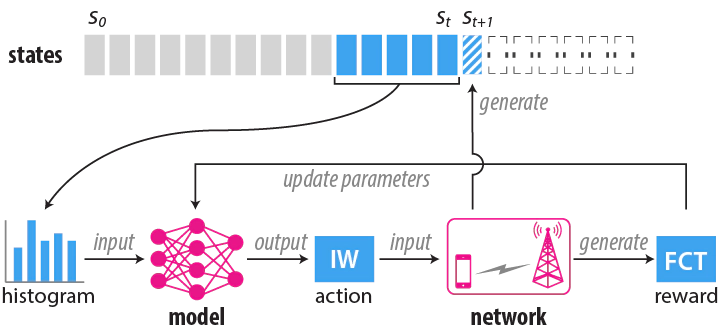
Mobile edge computing provides users with low response time and avoids unnecessary data transmission. Due to the deployment of 5G, the emerging edge systems can provide gigabit bandwidth. However, network protocols have not evolved together. In TCP, the initial congestion window (IW) is such a low value that most short flows still stay in slow start phase when finishing, and do not fully utilize available bandwidth. Naively increasing IW may result in congestion, which causes long latency. Moreover, since the network environment is dynamic, we have a challenging problem-how to adaptively adjust IW such that flow completion time is optimized, while congestion is minimized. In this paper, we propose an adaptive online decision method to solve the problem, which learns the best policy using deep reinforcement learning stably and fast. In addition, we propose an approach to further improve the performance by supervised learning, using data collected during online learning. We also propose to adopt SDN to address the challenges in implementing our method in MEC systems. To evaluate our method, we build an MEC simulator based on ns3. Our simulations demonstrate that our method performs better than existing methods. It can effectively reduce FCT with little congestion caused.